Functional Leg-Length Discrepancy Pads
The majority of people in the world actually have some degree of leg length discrepancy, up to 2cm. One study found that only around 1/4 of people have legs of equal lengths. LLD of greater than 2cm is relatively rare, however, and the greater the discrepancy, the greater the chances of having a clinical problem down the road. A limp generally begins when LLD exceeds 2cm and becomes extremely noticeable above 3cm. When patients with LLD develop an abnormal gait, one of the debilitating clinical features can be fatigue because of the relatively high amount of energy needed to walk in the new, inefficient way. Poliomyelitis, or polio, as it is more commonly known, used to account for around 1/3 of all cases of LLD, but due to the effectiveness of polio vaccines, it now represents a negligible cause of the condition. Functional LLD, described above, usually involves treatment focused on the hip, pelvis, and/or lower back, rather than the leg. If you have been diagnosed with functional LLD or pelvic obliquity, please ask your orthopaedic surgeon for more information about treatment of these conditions.

Causes
The causes of LLD are many, including a previous injury, bone infection, bone diseases (dysplasias), inflammation (arthritis) and neurologic conditions. Previously broken bones may cause LLD by healing in a shortened position, especially if the bone was broken in many pieces (comminuted) or if skin and muscle tissue around the bone were severely injured and exposed (open fracture). Broken bones in children sometimes grow faster for several years after healing, causing the injured bone to become longer. Also, a break in a child?s bone through a growth center (located near the ends of the bone) may cause slower growth, resulting in a shorter extremity. Bone infections that occur in children while they are growing may cause a significant LLD, especially during infancy. Bone diseases may cause LLD, as well; examples are neurofibromatosis, multiple hereditary exostoses and Ollier disease. Inflammation of joints during growth may cause unequal extremity length. One example is juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis, the joint degeneration that occurs in adults, very rarely causes a significant LLD.
Symptoms
LLD do not have any pain or discomfort directly associated with the difference of one leg over the other leg. However, LLD will place stress on joints throughout the skeletal structure of the body and create discomfort as a byproduct of the LLD. Just as it is normal for your feet to vary slightly in size, a mild difference in leg length is normal, too. A more pronounced LLD, however, can create abnormalities when walking or running and adversely affect healthy balance and posture. Symptoms include a slight limp. Walking can even become stressful, requiring more effort and energy. Sometimes knee pain, hip pain and lower back pain develop. Foot mechanics are also affected causing a variety of complications in the foot, not the least, over pronating, metatarsalgia, bunions, hammer toes, instep pain, posterior tibial tendonitis, and many more.
Diagnosis
The only way to decipher between anatomical and functional leg length inequalities (you can have both) is by a physical measurement and series of biomechanical tests. It is actually a simple process and gets to the true cause of some runner?s chronic foot, knee, hip and back pain. After the muscles are tested and the legs are measured it may be necessary to get a special X-ray that measures both of your thighs (Femurs) and legs (Tibias). The X-ray is read by a medical radiologist who provides a report of the actual difference down to the micrometer leaving zero room for error. Once the difference in leg length is known, the solution becomes clear.
Non Surgical Treatment
After the leg length discrepancy has been identified it can be categorized in as structural or functional and appropriate remedial action can be instigated. This may involve heel lifters or orthotics being used to level up the difference. The treatment of LLD depends on the symptoms being experienced. Where the body is naturally compensating for the LLD (and the patient is in no discomfort), further rectifying action may cause adverse effects to the biomechanical mechanism of the body causing further injury. In cases of functional asymmetry regular orthotics can be used to correct the geometry of the foot and ground contact. In structural asymmetry cases heel lifts may be used to compensate for the anatomic discrepancy.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is another option. In some cases the longer extremity can be shortened, but a major shortening may weaken the muscles of the extremity. In growing children, lower extremities can also be equalized by a surgical procedure that stops the growth at one or two sites of the longer extremity, while leaving the remaining growth undisturbed. Your physician can tell you how much equalization can be attained by surgically halting one or more growth centers. The procedure is performed under X-ray control through very small incisions in the knee area. This procedure will not cause an immediate correction in length. Instead, the LLD will gradually decrease as the opposite extremity continues to grow and "catch up." Timing of the procedure is critical; the goal is to attain equal length of the extremities at skeletal maturity, usually in the mid- to late teens. Disadvantages of this option include the possibility of slight over-correction or under-correction of the LLD and the patient?s adult height will be less than if the shorter extremity had been lengthened. Correction of significant LLDs by this method may make a patient?s body look slightly disproportionate because of the shorter legs.
Acquired Flat Foot Surgery
Overview
Most flat feet are not painful, particularly those flat feet seen in children. In the adult acquired flatfoot, pain occurs because soft tissues (tendons and ligaments) have been torn. The deformity progresses or worsens because once the vital ligaments and posterior tibial tendon are lost, nothing can take their place to hold up the arch of the foot. The painful, progressive adult acquired flatfoot affects women four times as frequently as men. It occurs in middle to older age people with a mean age of 60 years. Most people who develop the condition already have flat feet. A change occurs in one foot where the arch begins to flatten more than before, with pain and swelling developing on the inside of the ankle. Why this event occurs in some people (female more than male) and only in one foot remains poorly understood. Contributing factors increasing the risk of adult acquired flatfoot are diabetes, hypertension, and obesity. 
Causes
The posterior tibial tendon, which connects the bones inside the foot to the calf, is responsible for supporting the foot during movement and holding up the arch. Gradual stretching and tearing of the posterior tibial tendon can cause failure of the ligaments in the arch. Without support, the bones in the feet fall out of normal position, rolling the foot inward. The foot's arch will collapse completely over time, resulting in adult acquired flatfoot. The ligaments and tendons holding up the arch can lose elasticity and strength as a result of aging. Obesity, diabetes, and hypertension can increase the risk of developing this condition. Adult acquired flatfoot is seen more often in women than in men and in those 40 or older.
Symptoms
Pain and swelling behind the inside of your ankle and along your instep. You may be tender behind the inner ankle where the posterior tibial tendon courses and occasionally get burning, shooting, tingling or stabbing pain as a result of inflammation of the nerve inside the tarsal tunnel. Difficulty walking, the inability to walk long distances and a generalised ache while walking even short distances. This may probably become more pronounced at the end of each day. Change in foot shape, sometimes your tendon stretches out, this is due to weakening of the tendon and ligaments. When this occurs, the arch in your foot flattens and a flatfoot deformity occurs, presenting a change in foot shape. Inability to tip-toe, a way of diagnosing Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction is difficulty or inability to ?heel rise? (stand on your toes on one foot). Your tibialis posterior tendon enables you to perform this manoeuvre effectively. You may also experience pain upon attempting to perform a heel rise.
Diagnosis
In diagnosing flatfoot, the foot & Ankle surgeon examines the foot and observes how it looks when you stand and sit. Weight bearing x-rays are used to determine the severity of the disorder. Advanced imaging, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CAT or CT) scans may be used to assess different ligaments, tendons and joint/cartilage damage. The foot & Ankle Institute has three extremity MRI?s on site at our Des Plaines, Highland Park, and Lincoln Park locations. These extremity MRI?s only take about 30 minutes for the study and only requires the patient put their foot into a painless machine avoiding the uncomfortable Claustrophobia that some MRI devices create.
Non surgical Treatment
Orthotic or anklebrace, Over-the-counter or custom shoe inserts to position the foot and relieve pain are the most common non-surgical treatment option. Custom orthotics are often suggested if the shape change of the foot is more severe. An ankle brace (either over-the-counter or custom made) is another option that will help to ease tendon tension and pain. Boot immobilization. A walking boot supports the tendon and allows it to heal. Activity modifications. Depending on what we find, we may recommend limiting high-impact activities, such as running, jumping or court sports, or switching out high-impact activities for low-impact options for a period of time. Ice and anti-inflammatory medications. These may be given as needed to decrease your symptoms. 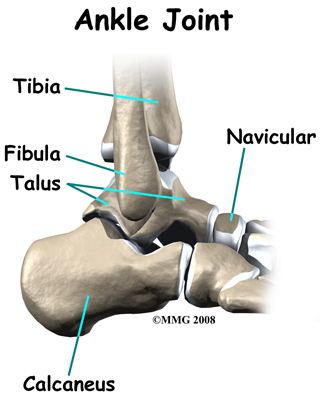
Surgical Treatment
A new type of surgery has been developed in which surgeons can re-construct the flat foot deformity and also the deltoid ligament using a tendon called the peroneus longus. A person is able to function fully without use of the peroneus longus but they can also be taken from deceased donors if needed. The new surgery was performed on four men and one woman. An improved alignment of the ankle was still evident nine years later, and all had good mobility 8 to 10 years after the surgery. None had developed arthritis.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Insufficiency Disorder
Overview Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of several terms to describe a painful, progressive flatfoot deformity in adults. Other terms include posterior tibial tendon insufficiency and adult acquired flatfoot. The term adult acquired flatfoot is more appropriate because it allows a broader recognition of causative factors, not only limited to the posterior tibial tendon, an event where the posterior tibial tendon looses strength and function. The adult acquired flatfoot is a progressive, symptomatic (painful) deformity resulting from gradual stretch (attenuation) of the tibialis posterior tendon as well as the ligaments that support the arch of the foot.  Causes As discussed above, many different problems can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to support the arch of your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use. Inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause a painful flatfoot. This type of arthritis attacks not only the cartilage in the joints, but also the ligaments that support the foot. Inflammatory arthritis not only causes pain, but also causes the foot to change shape and become flat. The arthritis can affect the back of the foot or the middle of foot, both of which can result in a fallen arch. An injury to the tendons or ligaments in the foot can cause the joints to fall out of alignment. The ligaments support the bones and prevent them from moving. If the ligaments are torn, the foot will become flat and painful. This more commonly occurs in the middle of the foot (Lisfranc injury), but can also occur in the back of the foot. Injuries to tendons of the foot can occur either in one instance (traumatically) or with repeated use over time (overuse injury). Regardless of the cause, if tendon function is altered, the forces that are transmitted across joints in the foot are changed and this can lead to increased stress on joint cartilage and ligaments. In addition to tendon and ligament injuries, fractures and dislocations of the bones in the midfoot can also lead to a flatfoot deformity. People with diabetes or with nerve problems that limits normal feeling in the feet, can have collapse of the arch or of the entire foot. This type of arch collapse is typically more severe than that seen in patients with normal feeling in their feet. In addition to the ligaments not holding the bones in place, the bones themselves can sometimes fracture and disintegrate without the patient feeling any pain. This may result in a severely deformed foot that is very challenging to correct with surgery. Special shoes or braces are the best method for dealing with this problem. Symptoms At first you may notice pain and swelling along the medial (big toe) side of the foot. This is where the posterior tibialis tendon travels from the back of the leg under the medial ankle bone to the foot. As the condition gets worse, tendon failure occurs and the pain gets worse. Some patients experience pain along the lateral (outside) edge of the foot, too. You may find that your feet hurt at the end of the day or after long periods of standing. Some people with this condition have trouble rising up on their toes. They may be unable to participate fully in sports or other recreational activities. Diagnosis Looking at the patient when they stand will usually demonstrate a flatfoot deformity (marked flattening of the medial longitudinal arch). The front part of the foot (forefoot) is often splayed out to the side. This leads to the presence of a ?too many toes? sign. This sign is present when the toes can be seen from directly behind the patient. The gait is often somewhat flatfooted as the patient has the dysfunctional posterior tibial tendon can no longer stabilize the arch of the foot. The physician?s touch will often demonstrate tenderness and sometimes swelling over the inside of the ankle just below the bony prominence (the medial malleolus). There may also be pain in the outside aspect of the ankle. This pain originates from impingement or compression of two tendons between the outside ankle bone (fibula) and the heel bone (calcaneus) when the patient is standing. Non surgical Treatment Although AAF is not reversible without surgery, appropriate treatment should address the patient?s current symptoms, attempt to reduce pain, and allow continued ambulation. In the early stages, orthotic and pedorthic solutions can address the loss of integrity of the foot?s support structures, potentially inhibiting further destruction.3-5 As a general principle, orthotic devices should only block or limit painful or destructive motion without reducing or restricting normal motion or muscle function. Consequently, the treatment must match the stage of the deformity.
Causes As discussed above, many different problems can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to support the arch of your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use. Inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause a painful flatfoot. This type of arthritis attacks not only the cartilage in the joints, but also the ligaments that support the foot. Inflammatory arthritis not only causes pain, but also causes the foot to change shape and become flat. The arthritis can affect the back of the foot or the middle of foot, both of which can result in a fallen arch. An injury to the tendons or ligaments in the foot can cause the joints to fall out of alignment. The ligaments support the bones and prevent them from moving. If the ligaments are torn, the foot will become flat and painful. This more commonly occurs in the middle of the foot (Lisfranc injury), but can also occur in the back of the foot. Injuries to tendons of the foot can occur either in one instance (traumatically) or with repeated use over time (overuse injury). Regardless of the cause, if tendon function is altered, the forces that are transmitted across joints in the foot are changed and this can lead to increased stress on joint cartilage and ligaments. In addition to tendon and ligament injuries, fractures and dislocations of the bones in the midfoot can also lead to a flatfoot deformity. People with diabetes or with nerve problems that limits normal feeling in the feet, can have collapse of the arch or of the entire foot. This type of arch collapse is typically more severe than that seen in patients with normal feeling in their feet. In addition to the ligaments not holding the bones in place, the bones themselves can sometimes fracture and disintegrate without the patient feeling any pain. This may result in a severely deformed foot that is very challenging to correct with surgery. Special shoes or braces are the best method for dealing with this problem. Symptoms At first you may notice pain and swelling along the medial (big toe) side of the foot. This is where the posterior tibialis tendon travels from the back of the leg under the medial ankle bone to the foot. As the condition gets worse, tendon failure occurs and the pain gets worse. Some patients experience pain along the lateral (outside) edge of the foot, too. You may find that your feet hurt at the end of the day or after long periods of standing. Some people with this condition have trouble rising up on their toes. They may be unable to participate fully in sports or other recreational activities. Diagnosis Looking at the patient when they stand will usually demonstrate a flatfoot deformity (marked flattening of the medial longitudinal arch). The front part of the foot (forefoot) is often splayed out to the side. This leads to the presence of a ?too many toes? sign. This sign is present when the toes can be seen from directly behind the patient. The gait is often somewhat flatfooted as the patient has the dysfunctional posterior tibial tendon can no longer stabilize the arch of the foot. The physician?s touch will often demonstrate tenderness and sometimes swelling over the inside of the ankle just below the bony prominence (the medial malleolus). There may also be pain in the outside aspect of the ankle. This pain originates from impingement or compression of two tendons between the outside ankle bone (fibula) and the heel bone (calcaneus) when the patient is standing. Non surgical Treatment Although AAF is not reversible without surgery, appropriate treatment should address the patient?s current symptoms, attempt to reduce pain, and allow continued ambulation. In the early stages, orthotic and pedorthic solutions can address the loss of integrity of the foot?s support structures, potentially inhibiting further destruction.3-5 As a general principle, orthotic devices should only block or limit painful or destructive motion without reducing or restricting normal motion or muscle function. Consequently, the treatment must match the stage of the deformity.  Surgical Treatment For patients with a more severe deformity, or significant symptoms that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgery may be necessary. There are several procedures available depending on the nature of your condition. Ligament and muscle lengthening, removal of inflamed tendon lining, transferring of a nearby tendon to re-establish an arch, and bone realignment and fusion are examples of surgical options to help with a painful flatfoot condition. Surgery can be avoided when symptoms are addressed early. If you are feeling ankle pain or notice any warmth, redness or swelling in your foot, contact us immediately. We can create a tailored treatment plan to resolve your symptoms and prevent future problems.
Surgical Treatment For patients with a more severe deformity, or significant symptoms that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgery may be necessary. There are several procedures available depending on the nature of your condition. Ligament and muscle lengthening, removal of inflamed tendon lining, transferring of a nearby tendon to re-establish an arch, and bone realignment and fusion are examples of surgical options to help with a painful flatfoot condition. Surgery can be avoided when symptoms are addressed early. If you are feeling ankle pain or notice any warmth, redness or swelling in your foot, contact us immediately. We can create a tailored treatment plan to resolve your symptoms and prevent future problems.